"Foreign Labor: Hidden Hands Building the Global Economy"

Introduction
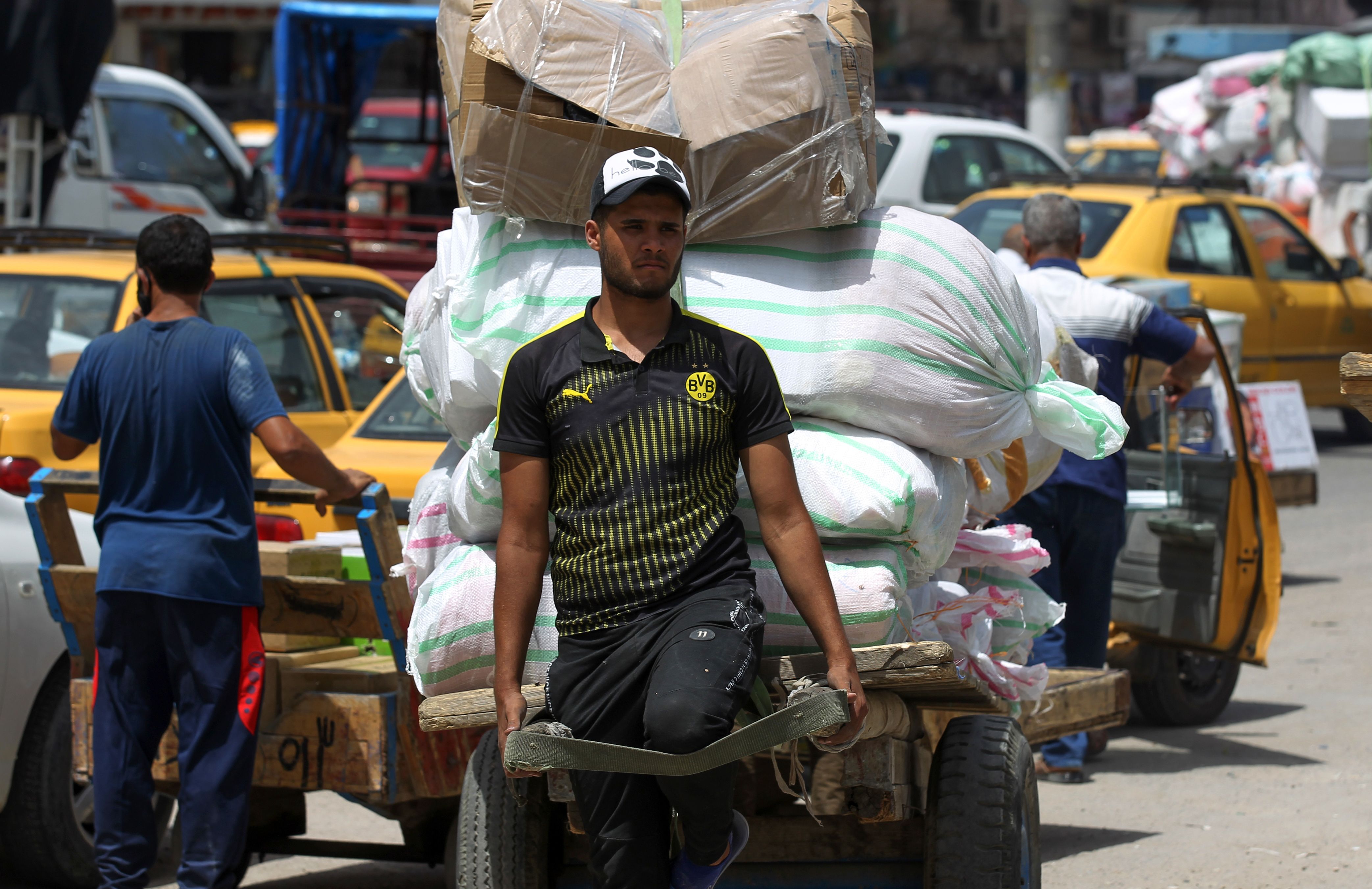
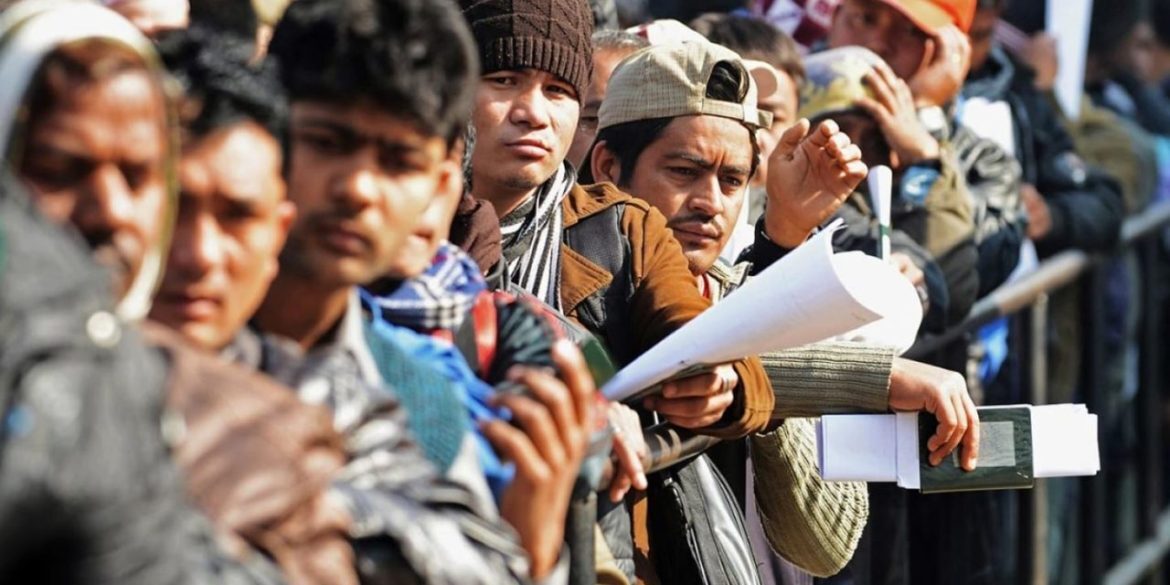
Foreign labor has become a crucial element in the global economy, contributing significantly to both the host countries and the countries of origin. While it offers many benefits, it also presents a host of challenges and complexities that need to be addressed. This investigative report delves into the multifaceted world of foreign labor, examining its economic impact, the challenges faced by foreign workers, and the policies governing their employment.
Economic Impact
Foreign labor plays a pivotal role in many economies. In countries like the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, foreign workers fill essential roles in industries such as construction, healthcare, agriculture, and domestic work. These workers often take on jobs that are less desirable to the local population, thus keeping these sectors functioning smoothly.For instance, in the GCC countries, foreign workers make up a significant portion of the workforce. In Saudi Arabia and the UAE, they constitute over 80% of the labor force in the private sector. This dependency on foreign labor is due to the rapid economic growth and development in these regions, which require a large workforce that the local population alone cannot supply.Moreover, remittances from foreign workers are a lifeline for many developing countries. According to the World Bank, global remittances reached $540 billion in 2020, providing critical support to millions of families worldwide. These funds help reduce poverty, improve

education and healthcare, and stimulate local economies.
Challenges Faced by Foreign Workers
Despite their significant contributions, foreign workers often face numerous challenges, including exploitation, discrimination, and poor working conditions. Many are subjected to low wages, long working hours, and lack of access to basic rights and services.A notable example is the kafala (sponsorship) system prevalent in many GCC countries, which ties workers to their employers and restricts their freedom to change jobs or leave the country without the employer’s consent. This system has been widely criticized for enabling abuse and exploitation of workers.Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can create significant hurdles for foreign workers, impacting their ability to integrate into the host society. They often face social isolation and may struggle to access healthcare, education, and legal protection.
Government Policies and Reforms
In recent years, there have been efforts to reform labor laws to better protect foreign workers. For example, Qatar has introduced significant changes to its labor system, including the abolition of the exit permit requirement and allowing workers to change jobs without employer permission. Similarly, the UAE has implemented measures to ensure timely payment of wages and improve working conditions.However, enforcement of these laws remains a challenge. Advocacy groups emphasize the need for more robust monitoring and enforcement mechanisms to ensure that these reforms translate into real improvements in workers' lives.
Conclusion
Foreign labor is an indispensable component of the global economy, providing essential services and contributing to economic growth in both host and origin countries. However, to maximize the benefits of foreign labor while minimizing its challenges, comprehensive and effective policies must be implemented and enforced. By addressing issues such as exploitation, discrimination, and poor working conditions, we can create a more equitable and just environment for all workers.
Recommendations
- Strengthen Labor Laws: Host countries should strengthen their labor laws to protect foreign workers' rights and ensure fair treatment.
- Improve Enforcement: Effective monitoring and enforcement mechanisms are essential to ensure compliance with labor laws and regulations.
- Promote Integration: Host countries should implement programs to help foreign workers integrate into society, including language classes and cultural orientation.
- Support from Origin Countries: Countries of origin should provide support to their citizens working abroad, including legal assistance and financial literacy programs.
- International Cooperation: Greater international cooperation is needed to address the challenges of foreign labor and ensure that workers' rights are protected globally.
By adopting these recommendations, we can work towards a future where the contributions of foreign workers are recognized and valued, and their rights are respected and upheld.
العمالة الأجنبية: أيدي تعمل في الظل وتبني الاقتصاد العالمي
المقدمة
أصبحت العمالة الأجنبية عنصرًا أساسيًا في الاقتصاد العالمي، تساهم بشكل كبير في كل من البلدان المضيفة وبلدان المنشأ. على الرغم من أنها تقدم العديد من الفوائد، إلا أنها تطرح أيضًا مجموعة من التحديات والتعقيدات التي تحتاج إلى معالجة. يتناول هذا التقرير التحقيقي العالم المتعدد الأوجه للعمالة الأجنبية، موضحًا تأثيرها الاقتصادي، والتحديات التي يواجهها العمال الأجانب، والسياسات التي تحكم توظيفهم.
التأثير الاقتصادي
تلعب العمالة الأجنبية دورًا محوريًا في العديد من الاقتصادات. في دول مثل الولايات المتحدة، المملكة المتحدة، ودول مجلس التعاون الخليجي، يملأ العمال الأجانب أدوارًا أساسية في صناعات مثل البناء، الرعاية الصحية، الزراعة، والعمل المنزلي. غالبًا ما يتولى هؤلاء العمال وظائف أقل رغبة لدى السكان المحليين، مما يحافظ على استمرار هذه القطاعات بسلاسة.على سبيل المثال، في دول مجلس التعاون الخليجي، يشكل العمال الأجانب نسبة كبيرة من القوى العاملة. في المملكة العربية السعودية والإمارات العربية المتحدة، يمثلون أكثر من 80٪ من القوة العاملة في القطاع الخاص. هذا الاعتماد على العمالة الأجنبية يعود إلى النمو الاقتصادي السريع والتنمية في هذه المناطق، التي تتطلب قوة عمل كبيرة لا يمكن أن توفرها السكان المحليين وحدهم.علاوة على ذلك، تعد الحوالات المالية من العمال الأجانب شريان حياة للعديد من الدول النامية. وفقًا للبنك الدولي، وصلت الحوالات المالية العالمية إلى 540 مليار دولار في عام 2020، مما وفر دعمًا حيويًا لملايين العائلات حول العالم. تساعد هذه الأموال في تقليل الفقر، وتحسين التعليم والرعاية الصحية، وتنشيط الاقتصادات المحلية.
التحديات التي يواجهها العمال الأجانب
على الرغم من مساهماتهم الكبيرة، يواجه العمال الأجانب العديد من التحديات، بما في ذلك الاستغلال، التمييز، وظروف العمل السيئة. يعاني الكثيرون من انخفاض الأجور، ساعات العمل الطويلة، وعدم الوصول إلى الحقوق والخدمات الأساسية.مثال بارز هو نظام الكفالة الموجود في العديد من دول مجلس التعاون الخليجي، الذي يربط العمال بأرباب عملهم ويقيد حريتهم في تغيير الوظائف أو مغادرة البلد دون إذن صاحب العمل. وقد تعرض هذا النظام لانتقادات واسعة لتمكينه من استغلال وإساءة معاملة العمال.بالإضافة إلى ذلك، تشكل الحواجز اللغوية والاختلافات الثقافية عوائق كبيرة للعمال الأجانب، مما يؤثر على قدرتهم على الاندماج في المجتمع المضيف. غالبًا ما يواجهون العزلة الاجتماعية وقد يكافحون للوصول إلى الرعاية الصحية، التعليم، والحماية القانونية.
سياسات وإصلاحات حكومية
في السنوات الأخيرة، كانت هناك جهود لإصلاح قوانين العمل لحماية العمال الأجانب بشكل أفضل. على سبيل المثال، أدخلت قطر تغييرات كبيرة على نظام العمل لديها، بما في ذلك إلغاء شرط تصريح الخروج والسماح للعمال بتغيير الوظائف دون إذن صاحب العمل. وبالمثل، نفذت الإمارات العربية المتحدة إجراءات لضمان دفع الأجور في الوقت المناسب وتحسين ظروف العمل.ومع ذلك، يبقى تطبيق هذه القوانين تحديًا. يؤكد مناصرو حقوق العمال على ضرورة وجود آليات مراقبة وتطبيق أكثر فعالية لضمان ترجمة هذه الإصلاحات إلى تحسينات حقيقية في حياة العمال.
الخاتمة
تعتبر العمالة الأجنبية مكونًا لا غنى عنه في الاقتصاد العالمي، حيث توفر خدمات أساسية وتسهم في النمو الاقتصادي في كل من الدول المضيفة وبلدان المنشأ. ومع ذلك، لتحقيق أقصى استفادة من العمالة الأجنبية وتقليل تحدياتها، يجب تنفيذ وتطبيق سياسات شاملة وفعالة. من خلال معالجة قضايا مثل الاستغلال، التمييز، وظروف العمل السيئة، يمكننا خلق بيئة أكثر عدالة وإنصافًا لجميع العمال.
التوصيات
- تعزيز قوانين العمل: يجب على الدول المضيفة تعزيز قوانين العمل لحماية حقوق العمال الأجانب وضمان معاملتهم بشكل عادل.
- تحسين التنفيذ: يجب أن تكون هناك آليات مراقبة وتطبيق فعالة لضمان الامتثال لقوانين العمل واللوائح.
- تشجيع الاندماج: يجب على الدول المضيفة تنفيذ برامج لمساعدة العمال الأجانب على الاندماج في المجتمع، بما في ذلك دروس اللغة والتوجيه الثقافي.
- دعم من دول المنشأ: يجب أن تقدم دول المنشأ الدعم لمواطنيها العاملين في الخارج، بما في ذلك المساعدة القانونية وبرامج التوعية المالية.
- التعاون الدولي: هناك حاجة إلى تعاون دولي أكبر لمعالجة تحديات العمالة الأجنبية وضمان حماية حقوق العمال على مستوى العالم.
من خلال تبني هذه التوصيات، يمكننا العمل نحو مستقبل يتم فيه الاعتراف بمساهمات العمال الأجانب وتقديرها، وضمان احترام حقوقهم وحمايتهم.